[Перевод] 8 наиболее распространенных структур данных в JavaScript
Звучит ли это знакомо: «Я начал заниматься веб разработкой после прохождения курсов»?
Возможно, вы хотите улучшить свои знания основ информатики в части структур данных и алгоритмов. Сегодня мы поговорим о некоторых наиболее распространенных структурах данных на примере JS.
1. Стек (вызовов) (Stack)
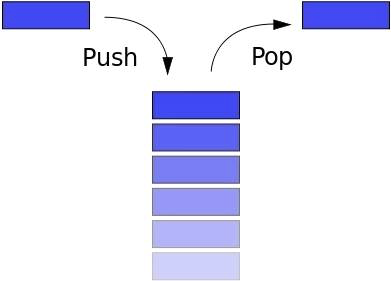
Стек следует принципу LIFO (Last In First Out — последним вошел, первым вышел). Если вы сложили книги друг на друга, и захотели взять самую нижнюю книгу, то сначала возьмете верхнюю, затем следующую и т.д. Кнопка «Назад» в браузере позволяет перейти (вернуться) на предыдущую страницу.
Стек имеет следующие методы:
- push: добавить новый элемент
- pop: удалить верхний элемент, вернуть его
- peek: вернуть верхний элемент
- length: вернуть количество элементов в стеке
Массив в JS имеет атрибуты стека, но мы построим его с нуля с помощью function Stack ():
function Stack() {
this.count = 0
this.storage = {}
this.push = function(value) {
this.storage[this.count] = value
this.count++
}
this.pop = function() {
if (this.count === 0) return undefined
this.count--
let result = this.storage[this.count]
delete this.storage[this.count]
return result
}
this.peek = function() {
return this.storage[this.count - 1]
}
this.size = function() {
return this.count
}
}
2. Очередь (кью) (Queue)

Очередь напоминает стек. Разница состоит в том, что очередь следует принципу FIFO (First In First Out — первым вошел, первым вышел). Когда вы стоите в очереди, первый в ней всегда будет первым.
Очередь имеет следующие методы:
- enqueue: войти в очередь, добавить элемент в конец
- dequeue: покинуть очередь, удалить первый элемент и вернуть его
- front: получить первый элемент
- isEmpty: проверить, пуста ли очередь
- size: получить количество элементов в очереди
Массив в JS имеет некоторые атрибуты очереди, поэтому мы можем использовать его для демонстрации:
function Queue() {
let collection = []
this.print = function() {
console.log(collection)
}
this.enqueue = function(element) {
collection.push(element)
}
this.dequeue = function() {
return collection.shift()
}
this.front = function() {
return collection[0]
}
this.isEmpty = function() {
return collection.length === 0
}
this.size = function() {
return collection.length
}
}
Порядок очередности (приоритет)
Очередь имеет продвинутую версию. Присвойте каждому элементу приоритет, и элементы будут отсортированы соответствующим образом:
function PriorityQueue() {
...
this.enqueue = function(element) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
collection.push(element)
} else {
let added = false
for (let i = 0; i < collection.length; i++) {
if (element[1] < collection[i][1]) {
collection.splice(i, 0, element)
added = true
break;
}
}
if (!added) {
collection.push(element)
}
}
}
}
Тестируем:
let pQ = new PriorityQueue()
pQ.enqueue([gannicus, 3])
pQ.enqueue([spartacus, 1])
pQ.enqueue([crixus, 2])
pQ.enqueue([oenomaus, 4])
pQ.print()
Результат:
[
[spartacus, 1],
[crixus, 2],
[gannicus, 3],
[oenomaus, 4]
]
3. Связный список (связанный, список узлов и ссылок или указателей) (Linked List)

Буквально, связный список — это цепочечная структура данных, где каждый узел состоит из двух частей: данных узла и указателя на следующий узел. Связный список и условный массив являются линейными структурами данных с сериализованным хранилищем. Отличия состоят в следующем:
Односвязный список имеет следующие методы:
- size: вернуть количество узлов
- head: вернуть первый элемент (head — голова)
- add: добавить элемент в конец (tail — хвост)
- remove: удалить несколько узлов
- indexOf: вернуть индекс узла
- elementAt: вернуть узел по индексу
- addAt: вставить узел в определенное место (по индексу)
- removeAt: удалить определенный узел (по индексу)
// узел
function Node(element) {
// данные
this.element = element
// указатель на следующий узел
this.next = null
}
function LinkedList() {
let length = 0
let head = null
this.size = function() {
return length
}
this.head = function() {
return head
}
this.add = function(element) {
let node = new Node(element)
if (head === null) {
head = node
} else {
let currentNode = head
while (currentNode.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
currentNode.next = node
}
length++
}
this.remove = function(element) {
let currentNode = head
let previousNode
if (currentNode.element !== element) {
head = currentNode.next
} else {
while (currentNode.element !== element) {
previousNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next
}
length--
}
this.isEmpty = function() {
return length === 0
}
this.indexOf = function(element) {
let currentNode = head
let index = -1
while (currentNode) {
index++
if (currentNode.element === element) {
return index
}
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return -1
}
this.elementAt = function(index) {
let currentNode = head
let count = 0
while (count < index) {
count++
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return currentNode.element
}
this.addAt = function(index, element) {
let node = new Node(element)
let currentNode = head
let previousNode
let currentIndex = 0
if (index > length) return false
if (index === 0) {
node.next = currentNode
head = node
} else {
while (currentIndex < index) {
currentIndex++
previousNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
node.next = currentNode
previousNode.next = node
}
length++
}
this.removeAt = function(index) {
let currentNode = head
let previousNode
let currentIndex = 0
if (index < 0 || index >= length) return null
if (index === 0) {
head = currentIndex.next
} else {
while (currentIndex < index) {
currentIndex++
previousNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next
}
length--
return currentNode.element
}
}
4. Коллекция (значений) (Set)

Коллекция (множество) — одна из основных концепций математики: набор хорошо определенных и обособленных объектов. ES6 представил коллекцию, которая имеет некоторое сходство с массивом. Тем не менее, коллекция не допускает включения повторяющихся элементов и не содержит индексов.
Стандартная коллекция имеет следующие методы:
- values: вернуть все элементы в коллекции
- size: вернуть количество элементов
- has: проверить, имеется ли элемент в коллекции
- add: добавить элемент
- remove: удалить элемент
- union: вернуть область пересечения двух коллекций
- difference: вернуть отличия двух коллекций
- subset: проверить, является ли одна коллекция подмножеством другой
// дистанцируемся от Set в JS
function MySet() {
let collection = []
this.has = function(element) {
return (collection.indexOf(element) !== -1)
}
this.values = function() {
return collection
}
this.size = function() {
return collection.length
}
this.add = function(element) {
if (!this.has(element)) {
collection.push(element)
return true
}
return false
}
this.remove = function(element) {
if (this.has(element)) {
index = collection.indexOf(element)
collection.splice(index, 1)
return true
}
return false
}
this.union = function(otherSet) {
let unionSet = new MySet()
let firstSet = this.values()
let secondSet = otherSet.values()
firstSet.forEach(i => unionSet.add(i))
secondSet.forEach(i => unionSet.add(i))
}
this.intersection = function(otherSet) {
let intersectionSet = new MySet()
let firstSet = this.values()
firstSet.forEach(function(e) {
if (otherSet.has(e)) {
intersectionSet.add(e)
}
})
return intersectionSet
}
this.difference = function(otherSet) {
let differenceSet = new MySet()
let firstSet = this.values()
firstSet.forEach(function(e) {
if (!otherSet.has(e)) {
differenceSet.add(e)
}
})
return differenceSet
}
this.subset = function(otherSet) {
lat firstSet = this.values()
return firstSet.every(value => otherSet.has(value))
}
}
5. Хеш-таблица (таблица кэширования) (Hash Table)

Хеш-таблица — это структура данных, которая строится по принципу ключ-значение. Из-за высокой скорости поиска значений по ключам, она используется в таких структурах, как Map, Dictionary и Object. Как показано на рисунке, хеш-таблица имеет hash function, преобразующую ключи в список номеров, которые используются как имена (значения) ключей. Время поиска значения по ключу может достигать O (1). Одинаковые ключи должны возвращать одинаковые значения — в этом суть функции хэширования.
Хеш-таблица имеет следующие методы:
- add: добавить пару ключ/значение
- remove: удалить пару
- lookup: найти значение по ключу
function hash(string, max) {
let hash = 0
for (let i = 0; i < string.length; i++) {
hash += string.charCodeAt(i)
}
return hash % max
}
function HashTable() {
let storage = []
const storageLimit = 4
this.add = function(key, value) {
let index = hash(key, storageLimit)
if (storage[index] === undefined) {
storage[index] = [
[key, value]
]
} else {
let inserted = false
for (let i = 0; i < storage[index].len; i++) {
if (storage[index][i][0] === key) {
storage[index][i][1] = value
inserted = true
}
}
if (inserted === false) {
storage[index].push([key, value])
}
}
}
this.remove = function(key) {
let index = hash(key, storageLimit)
if (storage[index].length === 1 && storage[index][0][0] === key) {
delete storage[index]
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < storage[index]; i++) {
if (storage[index][i][0] === key) {
delete storage[index][i]
}
}
}
}
this.lookup = function(key) {
let index = hash(key, storageLimit)
if (storage[index] === undefined) {
return undefined
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < storage[index].length; i++) {
if (storage[index][i][0] === key) {
return storage[index][i][1]
}
}
}
}
}
6. Дерево (Tree)

Древовидная структура — это многослойная (многоуровневая) структура. Это также нелинейная структура, в отличие от массива, стека и очереди. Данная структура очень эффективна в части добавления и поиска элементов. Вот некоторые концепции древовидной структуры:
- root: корневой элемент, не имеет «родителя»
- parent node: прямой узел верхнего слоя (уровня), может быть только одним
- child node: прямой узел (узлы) нижнего уровня, может быть несколько
- siblings: дочерние элементы одного родительского узла
- leaf: узел без «детей»
- Edge: ветка или ссылка (связь) между узлами
- Path: путь (совокупность ссылок) от начального узла до целевого элемента
- Height of Tree (высота дерева): количество ссылок самого длинного пути от определенного элемента до узла, не имеющего потомков
- Depth of Node (глубина узла): количество ссылок от корневого узла до определенного элемента
- Degree of Node: количество потомков
Вот пример двоичного дерева поиска (Binary Search Tree, BST). Каждый узел имеет только двоих потомков, левый (дочерний) узел меньше текущего (родительского), правый — больше:

Методами данного дерева являются следующие:
- add: добавить узел
- findMin: получить минимальный узел
- findMax: получить максимальный узел
- find: найти определенный узел
- isPresent: проверить наличие определенного узла
- remove: удалить узел
class Node {
constructor(data, left = null, right = null) {
this.data = data
this.left = left
this.right = right
}
}
class BST {
constructor() {
this.root = null
}
add(data) {
const node = this.root
if (node === null) {
this.root = new Node(data)
return
} else {
const searchTree = function(node) {
if (data < node.data) {
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = new Node(data)
return
} else if (node.left !== null) {
return searchTree(node.left)
}
} else if (data > node.data) {
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = new Node(data)
return
} else if (node.right !== null) {
return searchTree(node.right)
}
} else {
return null
}
}
return searchTree(node)
}
}
findMin() {
let current = this.root
while (current.left !== null) {
current = current.left
}
return current.data
}
findMax() {
let current = this.root
while (current.right !== null) {
current = current.right
}
return current.data
}
find(data) {
let current = this.root
while (current.data !== data) {
if (data < current.data) {
current = current.left
} else {
current = current.right
}
if (current === null) {
return null
}
}
return current
}
isPresent(data) {
let current = this.root
while (current) {
if (data === current.data) {
return true
}
data < current.data ? current = current.left : current = current.right
}
return false
}
remove(data) {
const removeNode = function(node, data) {
if (node === null) return null
if (data === node.data) {
// потомки отсутствуют
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) return null
// отсутствует левый узел
if (node.left === null) return node.right
// отсутствует правый узел
if (node.right === null) return node.left
// имеется два узла
let tempNode = node.right
while (tempNode.left !== null) {
tempNode = tempNode.left
}
node.data = tempNode.data
node.right = removeNode(node.right, tempNode.data)
return node
} else if (data < node.data) {
node.left = removeNode(node.right, data)
return node
} else {
node.right = removeNode(node.right, data)
return node
}
}
this.root = removeNode(this.root, data)
}
}
Тестируем:
const bst = new BST()
bst.add(4)
bst.add(2)
bst.add(6)
bst.add(1)
bst.add(3)
bst.add(5)
bst.add(7)
bst.remove(4)
console.log(bst.findMin())
console.log(bst.findMax())
bst.remove(7)
console.log(bst.findMax())
console.log(bst.isPresent(4))
Результат:
1
7
6
false
7. Нагруженное (префиксное) дерево (Trie, читается как «try»)

Префиксное дерево — это разновидность поискового дерева. Данные в нем сохраняются последовательно (шаг за шагом) — каждый узел дерева представляет собой один шаг. Префиксное дерево используется в словарях, поскольку существенно ускоряет поиск.
Каждый узел дерева — буква алфавита, следование по ветке приводит к формированию слова. Оно также содержит «булевый индикатор» для определения того, что текущий узел является последней буквой.
Префиксное дерево имеет следующие методы:
- add: добавить слово в словарь
- isWord: проверить наличие слова
- print: вернуть все слова
// узел дерева
function Node() {
this.keys = new Map()
this.end = false
this.setEnd = function() {
this.end = true
}
this.isEnd = function() {
return this.end
}
}
function Trie() {
this.root = new Node()
this.add = function(input, node = this.root) {
if (input.length === 0) {
node.setEnd()
return
} else if (!node.keys.has(input[0])) {
node.keys.set(input[0], new Node())
return this.add(input.substr(1), node.key.get(input[0]))
} else {
return this.add(input.substr(1), node.keys.get(input[0]))
}
}
this.isWord = function(word) {
let node = this.root
while (word.length > 1) {
if (node.keys.has(word[0])) {
return false
} else {
node = node.keys.get(word[0])
word = word.substr(1)
}
}
return (node.keys.has(word) && node.keys.get(word).isEnd()) ? true : false
}
this.print = function() {
let words = new Array()
let search = function(node = this.root, string) {
if (node.keys.size !== 0) {
for (let letter of node.keys.keys()) {
search(node.keys.get(letter), string.concat(letter))
}
if (node.isEnd()) {
words.push(string)
}
} else {
string.length > 0 ? words.push(string) : undefined
return
}
}
search(this.root, new String())
return words.length > 0 ? words : null
}
}
8. Граф (график) (Graph)

Граф, также известный как сеть (Network), представляет собой коллекцию связанных между собой узлов. Бывает два вида графов — ориентированный и неориентированный, в зависимости от того, имеют ли ссылки направление. Графы используются повсеместно, например, для расчета наилучшего маршрута в навигационных приложениях или для формирования списка рекомендаций в социальных сетях.
Графы могут быть представлены в виде списка или матрицы.
Список
В данном случае все родительские узлы располагаются слева, а их дочерние элементы справа.

Матрица
В данном случае узлы распределяются по строкам и столбцам, пересечение строки и столбца показывает отношение между узлами: 0 означает, что узлы не связаны между собой, 1 — узлы связаны.

Поиск по графу осуществляется двумя методами — поиск в ширину (Breath-First-Search, BFS) и поиск в глубину (Depth-First-Search, DFS).
Рассмотрим BFS:
function bfs(graph, root) {
let nodesLen = {}
for (let i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
nodesLen[i] = Infinity
}
nodesLen[root] = 0
let queue = [root]
let current
while (queue.length !== 0) {
current = queue.shift()
let curConnected = graph[current]
let neighborIdx = []
let idx = curConnected.indexOf(1)
while (idx !== -1) {
neighborIdx.push(idx)
idx = curConnected.indexOf(1, idx + 1)
}
for (let i = 0; i < neighborIdx.length; i++) {
if (nodesLen[neighborIdx[i]] === Infinity) {
nodesLen[neighborIdx[i]] = nodesLen[current] + 1
queue.push(neighborIdx[i])
}
}
}
return nodesLen
}
Тестируем:
let graph = [
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
]
console.log(bfs(graph, 1))
Результат:
{
0: 2,
1: 0,
2: 1,
3: 3,
4: Infinity
}
На этом у меня все. Надеюсь, вы нашли для себя что-то полезное. Счастливого кодинга!